- A substantial surge in cases has been reported.
- READ MORE: Researchers are urging further study into the possible side effects of Covid vaccines after a sudden increase in reported heart conditions.
In Victoria's agriculture industry, burgeoning.
The Department of Health has issued a warning regarding Q fever, a disease primarily transmitted from livestock to humans, specifically cattle, sheep, and goats.
There were 77 reported cases of Q fever in 2024, a 'significant increase' compared to the past five years.
Q fever is caused by infection with Coxiella burnetii bacteria, symptoms of which include a severe "flu-like illness" characterized by fever, sweats, chills, headaches, and joint pain.
The illness may lead to several long-term health problems, including heart disease, infections of the bones and joints, and infections of the blood vessels.
Between 10 and 15 percent of patients experienced chronic fatigue, also known as Q fever fatigue syndrome.
However, other patients may only experience minimal symptoms.
Although cases of the disease spreading from person to person are uncommon, it can be transmitted to humans by various domestic and wild animals, including kangaroos, cows, camels, rodents, cats, dogs, birds, and wallabies.
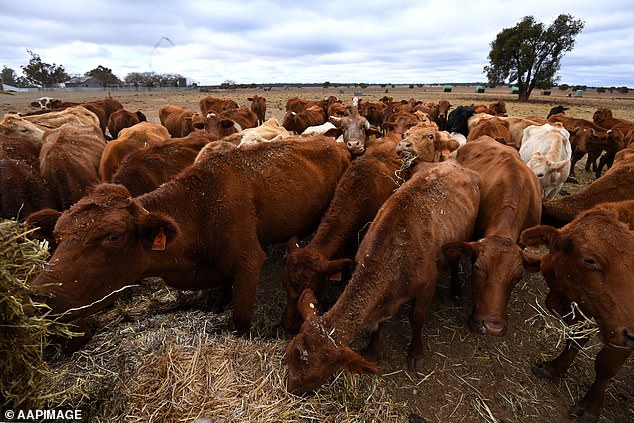
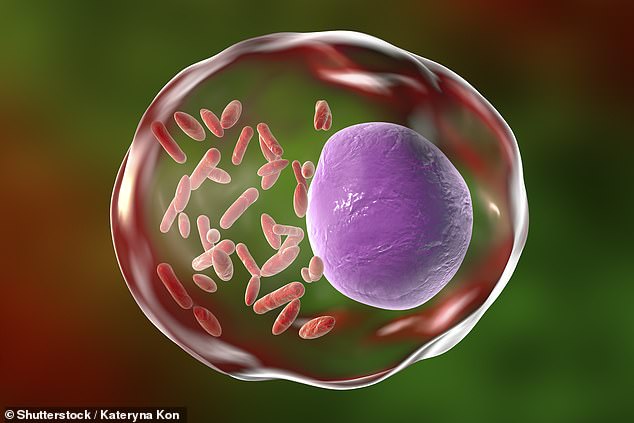

Those working closely with animals are at the greatest risk of exposure to Q fever, which is often spread through inhaling dust or aerosols contaminated with bacteria from the infected animals' birth fluids, feces, urine, or blood.
The state's health department called on agriculture, livestock, and dairy farm workers to immediately receive a vaccine against the disease.
'This applies to individuals in high-risk groups who would benefit from high-level protection against Q fever through vaccination,' it stated.
However, individuals who have previously contracted Q fever or have already received a Q fever vaccination should not receive the vaccine because of the risk of adverse reactions.
It is essential to undergo a screening process to determine previous exposure before administering a vaccination.
Treatment of Q fever can also be done with antibiotics.
Individuals who are at a high risk of exposure can decrease their chance of contraction by thoroughly washing their hands and arms with soap and water after any contact with animals.
Read more